QuantLib 金融计算——利率曲线之构建曲线(4)
介绍用 QuantLib 基于样本券的交易数据拟合出即期利率的非参数期限结构模型。
由于版本问题,代码可能与最新版不兼容。
如果未做特别说明,文中的程序都是 C++11 代码。
QuantLib 金融计算——利率曲线之构建曲线(4)
本文代码对应的 QuantLib 版本是 1.15。相关源代码可以在 QuantLibEx 找到。
概述
QuantLib 中提供了用三次 B 样条函数拟合期限结构的功能,但是,并未提供使用三次样条函数拟合期限结构的功能。本文展示了如何在 QuantLib 的框架内实现三次样条函数,并拟合期限结构。
示例所用的样本券交易数据来自专门进行期限结构分析的 R 包——termstrc。具体来说是数据集 govbonds 中的 GERMANY 部分,包含 2008-01-30 这一天德国市场上 52 只固息债的成交数据。
注意:为了适配 QuantLib,实际计算中删除了两只债券的数据,以保证所有样本券的到期时间均不相同。样本券数据在《利率曲线之构建曲线(3)》的附录中列出。
三次样条函数与期限结构
用三次样条函数拟合期限结构,实质上是用若干三次样条函数的组合近似贴现因子曲线的形状,
\[d(t,\beta) = 1 + \sum_{l=1}^n \beta_l c_l(t)\]贴现因子 $d(t,\beta)$ 表示为三次样条函数的线性组合,$\beta_l$ 是最优化计算需要估计出的参数。
三次样条函数 $c_l(t)$ 的形式基于文献 (Ferstl and Hayden, 2010),
\[\begin{cases} & \text{ if } l=n, c_l(t)=t\\ & \text{ else }, c_{l}\left(t\right)= \left\{\begin{array}{ll} 0 & {t<k_{l-1}} \\ {\frac{\left(t-k_{l-1}\right)^{3}}{6\left(k_{l}-k_{l-1}\right)}} & {k_{l-1} \leq t<k_{l}} \\ {\frac{\left(k_{l}-k_{l-1}\right)^{2}}{6}+\frac{\left(k_{l}-k_{l-1}\right)\left(t-k_{l}\right)}{2}+\frac{(t-k_l)^2}{2} -\frac{\left(t-k_{l}\right)^{3}}{6\left(k_{l+1}-k_{l}\right)}} & {k_{l} \leq t<k_{l+1}} \\ {\left(k_{l+1}-k_{l-1}\right)\left[\frac{2 k_{l+1}-k_{l}-k_{l-1}}{6}+\frac{t-k_{l+1}}{2}\right]} & {k_{l+1} \leq t} \end{array}\right. \end{cases}\]对于有 $n$ 个参数的贴现因子曲线,用户需要提供 $n-1$ 个 knots $k_i(1\le i\lt n)$,并令 $k_0 = 0$ 以及 $k_n = k_{n-1}$。
knots 的选择
knots 的选择基于文献 (McCulloch, 1975),也可以参考文献 (Ferstl and Hayden, 2010),
\[\begin{cases} & \text{ if } l=1, k_l = 0\\ & \text{ else if } l=n-1,k_l=m_N \\ & \text{ else }, k_l = m_h + \theta(m_{h+1} - m_h) \end{cases}\]其中,$h=\left\lceil\frac{(l-1) k}{n-2}\right\rceil$,$\theta=\frac{(l-1) k}{n-2}-h$,$n = \left\lfloor\sqrt{k}+0.5 \right\rfloor$,$m_i(1 \le i\le N)$ 是升序排列后样本券的剩余期限。
实现三次样条函数
三次样条函数类 CubicSpline 的实现仿照已存在的 BSpline 类,
CubicSpline.hpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
class CubicSpline {
public:
CubicSpline(const std::vector<Real>& knots);
~CubicSpline();
Real operator()(Natural i, Real x) const;
private:
Size n_;
std::vector<Real> knots_ex_;
};
CubicSpline.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
CubicSpline::CubicSpline(const std::vector<Real>& knots)
: n_(knots.size() + 1), knots_ex_(knots) {
knots_ex_.insert(knots_ex_.begin(), 0.0);
knots_ex_.insert(knots_ex_.end(), knots.back());
}
CubicSpline::~CubicSpline() {
}
Real CubicSpline::operator()(Natural i, Real x) const {
using namespace std;
if (i < n_) {
Real q = knots_ex_[i], q_minus = knots_ex_[i - 1], q_plus = knots_ex_[i + 1];
if (x < q_minus) {
return 0.0;
} else if (q_minus <= x and x < q) {
return pow(x - q_minus, 3) / (6.0 * (q - q_minus));
} else if (q <= x and x < q_plus) {
return pow(q - q_minus, 2) / 6.0
+ (q - q_minus) * (x - q) / 2.0
+ pow(x - q, 2) / 2.0
- pow(x - q, 3) / (6.0 * (q_plus - q));
} else {
return (q_plus - q_minus)
* ((2.0 * q_plus - q - q_minus) / 6.0
+ (x - q_plus) / 2.0);
}
} else {
return x;
}
}
实现拟合方法
拟合方法 CubicSplinesFitting 的实现仿照已存在的 CubicBSplinesFitting 类,两者均是 FittedBondDiscountCurve::FittingMethod 的派生类,
CubicSplinesFitting.hpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
class CubicSplinesFitting
: public FittedBondDiscountCurve::FittingMethod {
public:
CubicSplinesFitting(const std::vector<Time>& knotVector,
const Array& weights = Array(),
ext::shared_ptr<OptimizationMethod>
optimizationMethod = ext::shared_ptr<OptimizationMethod>(),
const Array& l2 = Array());
CubicSplinesFitting(const std::vector<Time>& knotVector,
const Array& weights,
const Array& l2);
//! cubic spline basis functions
Real basisFunction(Integer i, Time t) const;
static std::vector<Time> autoKnots(const std::vector<Time>& maturities);
#if defined(QL_USE_STD_UNIQUE_PTR)
std::unique_ptr<FittedBondDiscountCurve::FittingMethod> clone() const;
#else
std::auto_ptr<FittedBondDiscountCurve::FittingMethod> clone() const;
#endif
private:
Size size() const;
DiscountFactor discountFunction(const Array& x, Time t) const;
CubicSpline splines_;
Size size_;
//! N_th basis function coefficient to solve for when d(0)=1
Natural N_;
};
CubicSplinesFitting.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
CubicSplinesFitting::CubicSplinesFitting(const std::vector<Time>& knots,
const Array& weights,
ext::shared_ptr<OptimizationMethod> optimizationMethod,
const Array& l2)
: FittedBondDiscountCurve::FittingMethod(
false, weights, optimizationMethod, l2),
splines_(knots) {
Size basisFunctions = knots.size() + 1;
size_ = basisFunctions;
N_ = 0;
}
CubicSplinesFitting::CubicSplinesFitting(const std::vector<Time>& knots,
const Array& weights,
const Array& l2)
: FittedBondDiscountCurve::FittingMethod(
false, weights, ext::shared_ptr<OptimizationMethod>(), l2),
splines_(knots) {
Size basisFunctions = knots.size() + 1;
size_ = basisFunctions;
N_ = 0;
}
Real CubicSplinesFitting::basisFunction(Integer i,
Time t) const {
return splines_(i, t);
}
QL_UNIQUE_OR_AUTO_PTR<FittedBondDiscountCurve::FittingMethod> CubicSplinesFitting::clone() const {
return QL_UNIQUE_OR_AUTO_PTR<FittedBondDiscountCurve::FittingMethod>(
new CubicSplinesFitting(*this));
}
Size CubicSplinesFitting::size() const {
return size_;
}
DiscountFactor CubicSplinesFitting::discountFunction(const Array& x,
Time t) const {
DiscountFactor d = 1.0;
for (Size i = 0; i < size_; ++i) {
d += x[i] * splines_(i + 1, t);
}
return d;
}
std::vector<Time> CubicSplinesFitting::autoKnots(const std::vector<Time>& maturities) {
using namespace std;
vector<Time> m(maturities);
sort(m.begin(), m.end());
Size k = m.size();
Size n(floor(sqrt(k) + 0.5));
vector<Time> knots(n - 1);
knots[0] = 0.0;
knots[n - 1] = m.back();
for (Size l = 1; l < n - 1; ++l) {
Size h(ceil(Real(l * k) / Real(n - 2)));
Real theta = Real(l * k) / Real(n - 2) - h;
knots[l] = m[h - 1] + theta * (m[h] - m[h - 1]);
}
return knots;
}
测试
用上述两个类拟合样本券的期限结构,并和 termstrc 的结果做比较。
辅助函数 CubicSplineSpotRate 用于将样条函数表示的贴现因子转换成即期利率。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
QuantLib::Real CubicSplineSpotRate(const std::vector<QuantLib::Real>& knots,
const QuantLib::Array& weights,
const QuantLib::Time& t) {
using namespace std;
using namespace QuantLib;
CubicSpline spline(knots);
Size s = weights.size();
Real d = 1.0, r;
for (Size i = 0; i < s; ++i) {
d += weights[i] * spline(i + 1, t);
}
r = -std::log(d) / t;
return r;
}
测试函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
void TestCubicSplineFitting() {
using namespace std;
using namespace QuantLib;
// 样本券数据,以及相关配置
Size bondNum = 50;
vector<Real> cleanPrice = {
100.002, 99.92, 99.805, 99.75, 100.305, 99.76, 99.75, 99.975, 100.0416, 100.0574,
99.5049, 101.0971, 101.137, 100.7199, 99.8883, 100.908, 103.3553, 99.5034, 103.913, 97.4229,
104.5636, 99.7527, 104.3708, 99.6051, 104.8603, 101.3415, 105.29, 102.4969, 103.7602, 100.2803,
102.6046, 102.5291, 99.4748, 95.9702, 97.1815, 114.2849, 100.2847, 112.23, 98.397, 102.0235,
99.8483, 121.2711, 125.9157, 114.5791, 103.2202, 123.4668, 113.4694, 103.1873, 91.5603, 95.4441};
vector<Handle<Quote>> priceHandle(bondNum);
for (Size i = 0; i < bondNum; ++i) {
ext::shared_ptr<Quote> q(
new SimpleQuote(cleanPrice[i]));
Handle<Quote> hq(q);
priceHandle[i] = hq;
}
vector<Year> issueYear = {
2002, 2006, 2003, 2006, 1998, 2006, 2003, 2006, 1999, 2007,
2004, 2007, 1999, 2007, 2004, 2007, 1999, 2005, 2000, 2005,
2000, 2006, 2001, 2006, 2001, 2007, 2002, 2007, 2002, 2003,
2003, 2004, 2004, 2005, 2005, 1986, 2006, 1986, 2006, 2007,
2007, 1993, 1997, 1998, 1998, 2000, 2000, 2003, 2004, 2006};
vector<Month> issueMonth = {
Aug, Mar, Apr, May, Jul, Aug, Sep, Nov, Jan, Feb,
Feb, May, Jul, Aug, Aug, Sep, Oct, Feb, May, Aug,
Sep, Feb, May, Aug, Dec, Feb, Jun, Aug, Dec, Jun,
Oct, Apr, Oct, Apr, Oct, Jun, Apr, Sep, Oct, Apr,
Sep, Dec, Jul, Jan, Oct, Jan, Oct, Jan, Dec, Dec};
vector<Day> issueDay = {
14, 8, 11, 30, 4, 30, 25, 30, 4, 28, 2, 30, 4, 24, 25, 21, 22,
24, 5, 26, 29, 26, 23, 30, 28, 28, 26, 24, 31, 24, 21, 25, 27, 28,
30, 20, 26, 20, 31, 27, 21, 29, 3, 4, 7, 4, 27, 22, 24, 28};
vector<Year> maturityYear = {
2008, 2008, 2008, 2008, 2008, 2008, 2008, 2008, 2009, 2009,
2009, 2009, 2009, 2009, 2009, 2009, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010,
2011, 2011, 2011, 2011, 2012, 2012, 2012, 2012, 2013, 2013,
2014, 2014, 2015, 2015, 2016, 2016, 2016, 2016, 2017, 2017,
2018, 2024, 2027, 2028, 2028, 2030, 2031, 2034, 2037, 2039};
vector<Month> maturityMonth = {
Feb, Mar, Apr, Jun, Jul, Sep, Oct, Dec, Jan, Mar,
Apr, Jun, Jul, Sep, Oct, Dec, Jan, Apr, Jul, Oct,
Jan, Apr, Jul, Oct, Jan, Apr, Jul, Oct, Jan, Jul,
Jan, Jul, Jan, Jul, Jan, Jun, Jul, Sep, Jan, Jul,
Jan, Jan, Jul, Jan, Jul, Jan, Jan, Jul, Jan, Jul};
vector<Day> maturityDay = {
15, 14, 11, 13, 4, 12, 10, 12, 4, 13, 17, 12, 4, 11, 9, 11,
4, 9, 4, 8, 4, 8, 4, 14, 4, 13, 4, 12, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4,
20, 4, 20, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4};
vector<Date> issueDate(bondNum), maturityDate(bondNum);
for (Size i = 0; i < bondNum; ++i) {
Date idate(issueDay[i], issueMonth[i], issueYear[i]);
Date mdate(maturityDay[i], maturityMonth[i], maturityYear[i]);
issueDate[i] = idate;
maturityDate[i] = mdate;
}
vector<Real> couponRate = {
0.0425, 0.03, 0.03, 0.0325, 0.0475, 0.035, 0.035, 0.0375, 0.0375, 0.0375,
0.0325, 0.045, 0.045, 0.04, 0.035, 0.04, 0.05375, 0.0325, 0.0525, 0.025,
0.0525, 0.035, 0.05, 0.035, 0.05, 0.04, 0.05, 0.0425, 0.045, 0.0375, 0.0425,
0.0425, 0.0375, 0.0325, 0.035, 0.06, 0.04, 0.05625, 0.0375, 0.0425, 0.04,
0.0625, 0.065, 0.05625, 0.0475, 0.0625, 0.055, 0.0475, 0.04, 0.0425};
Frequency frequency = Annual;
Actual365Fixed dayCounter(Actual365Fixed::Standard);
BusinessDayConvention paymentConv = Unadjusted;
BusinessDayConvention terminationDateConv = Unadjusted;
BusinessDayConvention convention = Unadjusted;
Real redemption = 100.0;
Real faceAmount = 100.0;
Germany calendar(Germany::Eurex);
Date today = calendar.adjust(Date(30, Jan, 2008));
Settings::instance().evaluationDate() = today;
Natural bondSettlementDays = 0;
Date bondSettlementDate = calendar.advance(
today,
Period(bondSettlementDays, Days));
vector<ext::shared_ptr<BondHelper>> instruments(bondNum);
vector<Time> maturity(bondNum);
// 配置 helper
for (Size i = 0; i < bondNum; ++i) {
vector<Real> bondCoupon = {couponRate[i]};
Schedule schedule(
issueDate[i],
maturityDate[i],
Period(frequency),
calendar,
convention,
terminationDateConv,
DateGeneration::Backward,
false);
ext::shared_ptr<FixedRateBondHelper> helper(
new FixedRateBondHelper(
priceHandle[i],
bondSettlementDays,
faceAmount,
schedule,
bondCoupon,
dayCounter,
paymentConv,
redemption));
maturity[i] = dayCounter.yearFraction(
bondSettlementDate, helper->maturityDate());
instruments[i] = helper;
}
Real tolerance = 1.0e-6;
Natural max = 5000;
ext::shared_ptr<OptimizationMethod> optMethod(
new LevenbergMarquardt());
vector<Real> knots = CubicSplinesFitting::autoKnots(maturity);
vector<Real> termstrcKnotes = {
0.000000, 1.006027, 2.380274, 5.033425, 9.234521, 31.446575};
cout << "QuantLib knots:\t";
for (auto v : knots) {
cout << setprecision(6) << fixed << v << ", ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "termstrc knots:\t";
for (auto v : termstrcKnotes) {
cout << setprecision(6) << fixed << v << ", ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << endl;
CubicSplinesFitting csf(
knots, Array(), optMethod);
FittedBondDiscountCurve tsCubicSplines(
bondSettlementDate,
instruments, dayCounter,
csf, tolerance, max);
Array weights = tsCubicSplines.fitResults().solution();
Array termstrcWeights(7);
termstrcWeights[0] = 1.9320e-02, termstrcWeights[1] = -8.4936e-05,
termstrcWeights[2] = -3.2009e-04, termstrcWeights[3] = -3.7101e-04,
termstrcWeights[4] = 7.2921e-04, termstrcWeights[5] = 2.0159e-03,
termstrcWeights[6] = -4.1632e-02;
cout << "QuantLib weights: \t" << weights << endl;
cout << "termstrc weights: \t" << termstrcWeights << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "QuantLib final cost value:\t"
<< tsCubicSplines.fitResults().minimumCostValue() << endl;
cout << endl;
// 比较 QuantLib 和 termstrc 的结果
Real spotRate, termstrcSpot;
for (Size i = 0; i < bondNum; ++i) {
Time t = dayCounter.yearFraction(
bondSettlementDate, maturityDate[i]);
spotRate =
tsCubicSplines.zeroRate(t, Compounding::Continuous, frequency).rate() * 100.0;
termstrcSpot =
CubicSplineSpotRate(termstrcKnotes, termstrcWeights, t) * 100.0;
cout << setprecision(3) << fixed
<< t << ",\t"
<< spotRate << ",\t"
<< termstrcSpot << ",\t"
<< spotRate - termstrcSpot << endl;
}
}
部分结果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
QuantLib knots: 0.000000, 1.117808, 2.690411, 5.430137, 9.432877, 31.446575,
termstrc knots: 0.000000, 1.006027, 2.380274, 5.033425, 9.234521, 31.446575,
QuantLib weights: [ 0.005281; 0.004565; -0.002934; 0.000804; 0.000652; 0.001886; -0.038316 ]
termstrc weights: [ 0.019320; -0.000085; -0.000320; -0.000371; 0.000729; 0.002016; -0.041632 ]
QuantLib final cost value: 0.000338
0.044, 3.823, 4.125, -0.302
0.121, 3.809, 4.061, -0.253
0.197, 3.794, 4.001, -0.207
0.370, 3.761, 3.878, -0.116
...
..
.
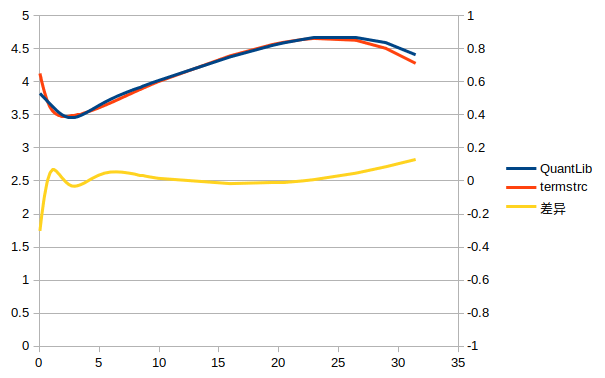
图 1:结果对比
注意:尽管以 termstrc 的结果作为基准,并不意味着基准就是正确答案。
由于样本券的数量不同(termstrc 使用了 52 只券),两者的 knots 差异较大。同时,因为优化方法的不同(termstrc 使用 OLS,QuantLib 使用 Levenberg-Marquardt 算法),估计出的参数也有差异。最终导致两个期限结构在两端差异较大。
不过,考虑到最终的 cost value,QuantLib 的结果可能更好一些。
参考文献
【1】Ferstl.R, Hayden.J (2010). “Zero-Coupon Yield Curve Estimation with the Package termstrc.” Journal of Statistical Software, Volume 36, Issue 1.
【2】McCulloch JH (1975). “The Tax-Adjusted Yield Curve.” The Journal of Finance, 30(3), 811–830.